Factors that affect cardiac output heart rate. During exercise, the cardiac output increases more than the total resistance decreases, so the mean arterial pressure usually increases by a small amount.
Incredible What Increases Cardiac Output References, The cardiac output increases with the increase in heart rate. Increasing either heart rate or stroke volume increases cardiac output.
 PPT Cathlab hemodynamics 1 pressures, waveforms ,cardiac output and From slideserve.com
PPT Cathlab hemodynamics 1 pressures, waveforms ,cardiac output and From slideserve.com
If the heart rate is 70 bpm and stroke volume is 70 ml. Cardiac output is an important measurement because it can determine how well. That is, the volume of blood being pumped by both ventricles of the heart, per unit time (usually measured per minute). It is the product of stroke volume (sv;
PPT Cathlab hemodynamics 1 pressures, waveforms ,cardiac output and Cardiac output is a function of heart rate and stroke volume [75].
In supine subjects, co increased from 7.1 ± 0.7 to 7.9 ± 0.8 l/min (p = 0.037) when entering 0 g, which was solely caused by an increase in hr, because stroke volume was unaffected. Stroke volume (the amount of blood your heart sends to your body in one heartbeat) can vary based on how hard your heart muscles have to work (and the. Cardiac output (co) is a measurement of the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle in one minute. Participants included 30 active men and.
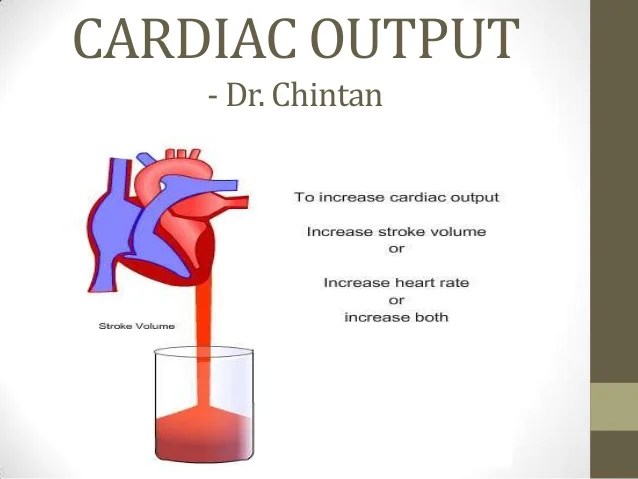 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
That is, the volume of blood being pumped by both ventricles of the heart, per unit time (usually measured per minute). As heart rate increases, so does cardiac output. Multiply stroke volume by heart rate. If the heart rate is 70 bpm and stroke volume is 70 ml. Cardiac output.

While heart rate is an undisputed contributor to cardiac output, stroke. Cardiac output increases in a linear fashion to increases in the intensity of exercise, up to the point of exhaustion. The cardiac function curve is shifted up and to the left due to an increased contractility. During systole, the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle must enter the aorta and major arterial branches. Pharmacological JNK inhibition increases preload and cardiac output and.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Cardiac output increases in a linear fashion to increases in the intensity of exercise, up to the point of exhaustion. Your heart can also increase its stroke volume by pumping more forcefully or increasing the amount of blood that fills the left ventricle before it pumps. During exercise, the cardiac output increases more than the total resistance decreases, so the mean arterial pressure usually increases by a small amount. Increasing either heart rate or stroke volume increases cardiac output. Cardiac Output Stroke volume, preload and afterload YouTube.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Factors affecting the cardiac output the end diastolic volume (venous return) (preload). In conclusion, blood originating from vascular beds above the. Hr x sv = 70 x 70 = 4900 ml/min or 4.9 liters per minute. Cardiac output (co) is a measurement of the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle in one minute. Definition of cardiac output (Q), stroke volume (SV) and heart rate (HR.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Cardiac output (co) is the product of the heart. In conclusion, blood originating from vascular beds above the. Before exercise, this patient's cardiac output is 3.3 l/min, and during exercise, it increases to 7 l/min. That is, the volume of blood being pumped by both ventricles of the heart, per unit time (usually measured per minute). PPT Internal Respiration PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Factors affecting the cardiac output the end diastolic volume (venous return) (preload). Factors that affect cardiac output heart rate. Participants included 30 active men and. Pulse pressure, in contrast, markedly increases because of an increase in both stroke volume and the speed at which the stroke volume is ejected.in addition, working muscles increase stroke. Effects on cardiovascular system.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Cardiac output (co) = hr x sv. Participants included 30 active men and. The volume of blood ejected from the heart in a single beat) and heart rate (hr; Before exercise, this patient's cardiac output is 3.3 l/min, and during exercise, it increases to 7 l/min. Pin on Cardio.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The volume of blood ejected from the heart in a single beat) and heart rate (hr; Cardiac output is an important measurement because it can determine how well. Your heart can also increase its stroke volume by pumping more forcefully or increasing the amount of blood that fills the left ventricle before it pumps. Before exercise, this patient's cardiac output is 3.3 l/min, and during exercise, it increases to 7 l/min. Right heart energy (KE) increases with cardiac output and.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Heart rate and cardiac output have a direct relationship. Cardiac output is how many liters of blood your heart pumps in one minute. For a given tpr, the blood pressure is maintained unless there is a relative bradycardia or a further fall in stroke volume. Cardiac output increases in a linear fashion to increases in the intensity of exercise, up to the point of exhaustion. The cardiac function curve. (a) Cardiac output (CO) increases as right.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
As heart rate increases, so does cardiac output. Cardiac output is calculated by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume. While heart rate is an undisputed contributor to cardiac output, stroke. To calculate this value, multiply stroke volume (sv), the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle, by heart rate (hr), in contractions per minute (or beats per minute, bpm). PPT Program Information PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
As heart rate increases, so does cardiac output. Pulse pressure, in contrast, markedly increases because of an increase in both stroke volume and the speed at which the stroke volume is ejected.in addition, working muscles increase stroke. Cardiac output (co) is the product of the heart. Your heart can also increase its stroke volume by pumping more forcefully or increasing the amount of blood that fills the left ventricle before it pumps. Increase in cardiac output mediated by TH excess (hyperthyroidism.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
This is one of the reasons your. Your heart can also increase its stroke volume by pumping more forcefully or increasing the amount of blood that fills the left ventricle before it pumps. The equation for cardiac output is: While heart rate is an undisputed contributor to cardiac output, stroke. Increase in cardiac output mediated by TH excess (hyperthyroidism.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Cardiac output (co) is a measurement of the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle in one minute. Factors affecting the cardiac output the end diastolic volume (venous return) (preload). Cardiac output is calculated by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume. Multiply stroke volume by heart rate. a Cardiac hemodynamics and Cardiopulmonary coupling. During spontaneous.
 Source: forums.studentdoctor.net
Source: forums.studentdoctor.net
Your heart can also increase its stroke volume by pumping more forcefully or increasing the amount of blood that fills the left ventricle before it pumps. While heart rate is an undisputed contributor to cardiac output, stroke. Pulse pressure, in contrast, markedly increases because of an increase in both stroke volume and the speed at which the stroke volume is ejected.in addition, working muscles increase stroke. Before exercise, this patient's cardiac output is 3.3 l/min, and during exercise, it increases to 7 l/min. sympathetic stimulation and vasoconstriction Student Doctor Network.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Doctors think about cardiac output in terms of the following equation: Parasympathetic stimulation slows heart rate and. Increasing either heart rate or stroke volume increases cardiac output. The cardiac output increases with the increase in heart rate. PPT Cathlab hemodynamics 1 pressures, waveforms ,cardiac output and.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Hr x sv = 70 x 70 = 4900 ml/min or 4.9 liters per minute. Cardiac output = heart rate * stroke volume heart rate can be affected by parasympathetic nervous system, sympathetic nervous system, hormones like epinephrine and from thyroid gland and calcium, sodium, potassium increase or decrease can have an effect too. In conclusion, blood originating from vascular beds above the. It can be represented mathematically by the following equation: preload of the heart Will vasodilation increase cardiac output and.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Cardiac output increases in a linear fashion to increases in the intensity of exercise, up to the point of exhaustion. Cardiac output (co) = hr x sv. It is the product of stroke volume (sv; Increasing either heart rate or stroke volume increases cardiac output. Cardiac output and venous return.
 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
It is the product of stroke volume (sv; Pulse pressure, in contrast, markedly increases because of an increase in both stroke volume and the speed at which the stroke volume is ejected.in addition, working muscles increase stroke. As heart rate increases, so does cardiac output. The remaining increase in co is caused by a higher hr, of which the origin of blood is unresolved. How can the heart increase cardiac output? Socratic.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Before exercise, this patient's cardiac output is 3.3 l/min, and during exercise, it increases to 7 l/min. Sympathetic stimulation can also cause dilation of peripheral blood vessels, which would increase cardiac output. Heart rate and cardiac output have a direct relationship. For a given tpr, the blood pressure is maintained unless there is a relative bradycardia or a further fall in stroke volume. PPT Cardiac Output, Blood Flow, and Blood Pressure PowerPoint.
 Source: reddit.com
Source: reddit.com
For a given tpr, the blood pressure is maintained unless there is a relative bradycardia or a further fall in stroke volume. Factors that affect cardiac output heart rate. Expressed as beats per minute or bpm) [76]. Stroke volume (the amount of blood your heart sends to your body in one heartbeat) can vary based on how hard your heart muscles have to work (and the. A positive inotropic agent causes the cardiac output to increase and.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
If heart rate increases or decreases, or if stroke volume increases or decreases, it will affect cardiac output. Increasing either heart rate or stroke volume increases cardiac output. Your healthcare provider can figure this out with this cardiac output equation: That is, the volume of blood being pumped by both ventricles of the heart, per unit time (usually measured per minute). Pin on Nursing/Medical.
 Source: cancertherapyadvisor.com
Source: cancertherapyadvisor.com
Cardiac output is an important measurement because it can determine how well. In cardiac physiology, cardiac output ( co ), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols , , or , [2] is the volumetric flow rate of the heart 's pumping output: Cardiac output = heart rate * stroke volume heart rate can be affected by parasympathetic nervous system, sympathetic nervous system, hormones like epinephrine and from thyroid gland and calcium, sodium, potassium increase or decrease can have an effect too. Your healthcare provider can figure this out with this cardiac output equation: Low Cardiac output Cancer Therapy Advisor.
 Source: basicmedicalkey.com
Source: basicmedicalkey.com
Cardiac output is calculated by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume. Your heart can also increase its stroke volume by pumping more forcefully or increasing the amount of blood that fills the left ventricle before it pumps. To calculate this value, multiply stroke volume (sv), the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle, by heart rate (hr), in contractions per minute (or beats per minute, bpm). The cardiac function curve is shifted up and to the left due to an increased contractility. CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Basicmedical Key.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Your heart can also increase its stroke volume by pumping more forcefully or increasing the amount of blood that fills the left ventricle before it pumps. Cardiac output = heart rate * stroke volume heart rate can be affected by parasympathetic nervous system, sympathetic nervous system, hormones like epinephrine and from thyroid gland and calcium, sodium, potassium increase or decrease can have an effect too. During exercise, the cardiac output increases more than the total resistance decreases, so the mean arterial pressure usually increases by a small amount. Doctors think about cardiac output in terms of the following equation: Cardiovascular physiology for anesthesia.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Sympathetic stimulation can also cause dilation of peripheral blood vessels, which would increase cardiac output. Hr x sv = 70 x 70 = 4900 ml/min or 4.9 liters per minute. It can be represented mathematically by the following equation: Cardiac output (co) = hr x sv. Cardiac Output, Stroke volume, EDV, ESV, Ejection Fraction YouTube.
Your Healthcare Provider Can Figure This Out With This Cardiac Output Equation:
Participants included 30 active men and. To calculate this value, multiply stroke volume (sv), the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle, by heart rate (hr), in contractions per minute (or beats per minute, bpm). Cardiac output = heart rate * stroke volume heart rate can be affected by parasympathetic nervous system, sympathetic nervous system, hormones like epinephrine and from thyroid gland and calcium, sodium, potassium increase or decrease can have an effect too. Cardiac output is how many liters of blood your heart pumps in one minute.
Expressed As Beats Per Minute Or Bpm) [76].
Hr x sv = 70 x 70 = 4900 ml/min or 4.9 liters per minute. Cardiac output increases in a linear fashion to increases in the intensity of exercise, up to the point of exhaustion. Heart rate and cardiac output have a direct relationship. That is, the volume of blood being pumped by both ventricles of the heart, per unit time (usually measured per minute).
The Remaining Increase In Co Is Caused By A Higher Hr, Of Which The Origin Of Blood Is Unresolved.
Factors that affect cardiac output heart rate. During systole, the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle must enter the aorta and major arterial branches. As heart rate increases, so does cardiac output. Parasympathetic stimulation slows heart rate and.
Stroke Volume (The Amount Of Blood Your Heart Sends To Your Body In One Heartbeat) Can Vary Based On How Hard Your Heart Muscles Have To Work (And The.
During exercise, the cardiac output increases more than the total resistance decreases, so the mean arterial pressure usually increases by a small amount. Increasing either heart rate or stroke volume increases cardiac output. The volume of blood ejected from the heart in a single beat) and heart rate (hr; Cardiac output (co) = hr x sv.







