Anaerobic respiration is the type of respiration through which cells can break down sugars to generate energy in the absence of oxygen. Electrons are transferred to oxygen using the.
15 Min What Does Aerobic Respiration Mean In Biology For Diet, This process includes the krebs cycle, electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation. The process in which glucose is converted into co2 and h2o in the presence of oxygen, releasing large amounts of atp.

The process in which glucose is converted into co2 and h2o in the presence of oxygen, releasing large amounts of atp. As already stated, cellular respiration can be of two types: Aerobic respiration is more efficient than. Electrons are transferred to oxygen using the.
What Is The Definition Of Cellular Respiration In Biology SHOTWERK Biology glossary search by everythingbio.com :
The highlights of krebs cycle are. Anaerobic respiration is the type of respiration through which cells can break down sugars to generate energy in the absence of oxygen. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, whereas anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. It is the release of a relatively large amount of energy in cells by the breakdown of food substances in the presence of oxygen:
 Source: tessshebaylo.com
Source: tessshebaylo.com
It is a type of respiration that requires oxygen to occur, and produces water, carbon dioxide and atp. There are four stages to aerobic respiration: The highlights of krebs cycle are. It is a cyclic aerobic process taking place in the matrix of mitochondria to break down pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide in the presence of certain enzymes. Balanced Chemical Equation For Anaerobic Respiration In Animals.
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
It takes place in the matrix of mitochondria. There are four stages to aerobic respiration: This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals. This is in contrast to the highly efficient process of aerobic respiration, which relies on oxygen to produce energy. Aerobic Respiration The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Aerobic respiration is more efficient than. Anaerobic respiration is the type of respiration through which cells can break down sugars to generate energy in the absence of oxygen. Cellular respiration involves breakdown of glucose into carbon dioxide and water in presence of oxygen, releasing energy. Aerobic respiration respiration using oxygen to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration. Cellular Respiration.
 Source: wasfa-hd.blogspot.com
Source: wasfa-hd.blogspot.com
Most of the plant and animal cells use aerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondria and the cytoplasm of the cell. Respiration is also a cellular process. The cycle involves a series of changes in organic acids with 4‐, 5‐, and 6‐ carbon atoms (citric acid has 6 carbons). Where Is The Energy Stored In Atp Quizlet Wasfa Blog.
 Source: abcworksheet.com
Source: abcworksheet.com
Cellular respiration describes how cells produce adenosine triphosphate (atp), which is cellular energy and can occur. Electrons are transferred to oxygen using the. It is the release of a relatively large amount of energy in cells by the breakdown of food substances in the presence of oxygen: This process includes the krebs cycle, electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation. Cellular Respiration Process.
 Source: cancercelltreatment.com
Source: cancercelltreatment.com
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, whereas anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. Other articles where aerobic respiration is discussed: It is the release of a relatively large amount of energy in cells by the breakdown of food substances in the presence of oxygen: On the other hand, anaerobic bacteria, yeast cells, prokaryotes, and muscle cells perform anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic Vs Aerobic Do You Have Pathogens? Why?.
 Source: shotwerk.blogspot.com
Source: shotwerk.blogspot.com
Electrons are transferred to oxygen using the. The sugar is completely broken down to carbon dioxide and water, yielding a maximum of 38 molecules of atp per molecule of glucose. Thus, it is also called a citric acid cycle. What does aerobic mean in biology? Meaning Of Cellular Respiration In English SHOTWERK.
 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
The first step in is glycolysis, the second is the citric acid cycle and the third is the electron trans port system. The highlights of krebs cycle are. It is a type of respiration that requires oxygen to occur, and produces water, carbon dioxide and atp. Aerobic respiration is the process through which glucose is burned or oxidised in the presence of oxygen to produce energy (atp). Net yield of aerobic respiration during Krebs cycle class 11 biology CBSE.
 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
Thus, it is also called a citric acid cycle. This type of respiration is common in most plants and animals, including humans, birds and other mammals. Aerobic respiration is more efficient than. This is in contrast to the highly efficient process of aerobic respiration, which relies on oxygen to produce energy. Aerobic And Anaerobic Respiration Major Differences.
 Source: abcworksheet.com
Source: abcworksheet.com
The cycle involves a series of changes in organic acids with 4‐, 5‐, and 6‐ carbon atoms (citric acid has 6 carbons). Oxygen carried by blood is used in cellular respiration and carbon dioxide released combines with hemoglobin in rbcs. Cellular respiration describes how cells produce adenosine triphosphate (atp), which is cellular energy and can occur. Molecular oxygen is the most efficient electron acceptor for respiration, due to. Cellular Respiration Summary ABC Worksheet.
 Source: shotwerk.blogspot.com
Source: shotwerk.blogspot.com
Cellular respiration describes how cells produce adenosine triphosphate (atp), which is cellular energy and can occur. Aerobic respiration is the process through which glucose is burned or oxidised in the presence of oxygen to produce energy (atp). Respiration is also a cellular process. The cycle takes place in the mitochondria, separated from the. What Is Cellular Respiration Mean In Science SHOTWERK.
 Source: shotwerk.blogspot.com
Source: shotwerk.blogspot.com
Thus, it is also called a citric acid cycle. The sugar is completely broken down to carbon dioxide and water, yielding a maximum of 38 molecules of atp per molecule of glucose. Cellular respiration involves breakdown of glucose into carbon dioxide and water in presence of oxygen, releasing energy. Aerobic respiration respiration using oxygen to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration. Meaning Of Cellular Respiration In English SHOTWERK.

This is in contrast to the highly efficient process of aerobic respiration, which relies on oxygen to produce energy. Aerobic respiration is more efficient than. Oxygen carried by blood is used in cellular respiration and carbon dioxide released combines with hemoglobin in rbcs. Heterotrophic metabolism:.most familiar respiratory process (aerobic respiration) uses oxygen as the final electron acceptor. Aerobic Respiration Bio Anatomical Vector Illustration Diagram Labeled.

The cycle takes place in the mitochondria, separated from the. Aerobic respiration is the process through which glucose is burned or oxidised in the presence of oxygen to produce energy (atp). Cells break down food in the mitochondria in a long, multistep process that produces roughly 36 atp. Oxygen carried by blood is used in cellular respiration and carbon dioxide released combines with hemoglobin in rbcs. What does aerobic respiration produce? Quora.
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
The first step in is glycolysis, the second is the citric acid cycle and the third is the electron trans port system. If oxygen is present, the pyruvate produced in glycolysis is oxidized further in the krebs cycle, a continuation of aerobic respiration. Glycolysis, the link reaction, the krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. The highlights of krebs cycle are. Anaerobic Respiration The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary.
 Source: biodifferences.net
Source: biodifferences.net
It is a cyclic aerobic process taking place in the matrix of mitochondria to break down pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide in the presence of certain enzymes. Aerobic respiration is more efficient than. Citric acid is the first product of this cycle. As already stated, cellular respiration can be of two types: Difference between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Bio Differences.

There are four stages to aerobic respiration: Deoxygenated or impure blood is carried by veins to the lungs to be converted into oxygenated blood. This is in contrast to the highly efficient process of aerobic respiration, which relies on oxygen to produce energy. Glycolysis, the link reaction, the krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Does the oxygen we inhale disappear in our body? Quora.

Oxygen carried by blood is used in cellular respiration and carbon dioxide released combines with hemoglobin in rbcs. Most of the plant and animal cells use aerobic respiration. It takes place in the matrix of mitochondria. What does aerobic mean in biology? Anaerobic Energy Production During Exercise Occurs During A Process.
 Source: liberaldictionary.com
Source: liberaldictionary.com
The sugar is completely broken down to carbon dioxide and water, yielding a maximum of 38 molecules of atp per molecule of glucose. It is a cyclic aerobic process taking place in the matrix of mitochondria to break down pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide in the presence of certain enzymes. It is a type of respiration that requires oxygen to occur, and produces water, carbon dioxide and atp. There are four stages to aerobic respiration: aerobic respiration Liberal Dictionary.
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
The cycle involves a series of changes in organic acids with 4‐, 5‐, and 6‐ carbon atoms (citric acid has 6 carbons). Thus, it is also called a citric acid cycle. The process in which glucose is converted into co2 and h2o in the presence of oxygen, releasing large amounts of atp. This is in contrast to the highly efficient process of aerobic respiration, which relies on oxygen to produce energy. Aerobic Respiration The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary.

Aerobic respiration is the process through which glucose is burned or oxidised in the presence of oxygen to produce energy (atp). There are four stages to aerobic respiration: Most of the plant and animal cells use aerobic respiration. It takes place in the matrix of mitochondria. What Is The Definition Of Cellular Respiration In Biology SHOTWERK.
 Source: abcworksheet.com
Source: abcworksheet.com
It is a cyclic aerobic process taking place in the matrix of mitochondria to break down pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide in the presence of certain enzymes. Cellular respiration involves breakdown of glucose into carbon dioxide and water in presence of oxygen, releasing energy. On the other hand, anaerobic bacteria, yeast cells, prokaryotes, and muscle cells perform anaerobic respiration. The sugar is completely broken down to carbon dioxide and water, yielding a maximum of 38 molecules of atp per molecule of glucose. Cellular Respiration Process.
 Source: janathurahman.weebly.com
Source: janathurahman.weebly.com
The sugar is completely broken down to carbon dioxide and water, yielding a maximum of 38 molecules of atp per molecule of glucose. This process includes the krebs cycle, electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation. The highlights of krebs cycle are. Cells break down food in the mitochondria in a long, multistep process that produces roughly 36 atp. Aerobic Metabolism Principle Of Biochemistry.
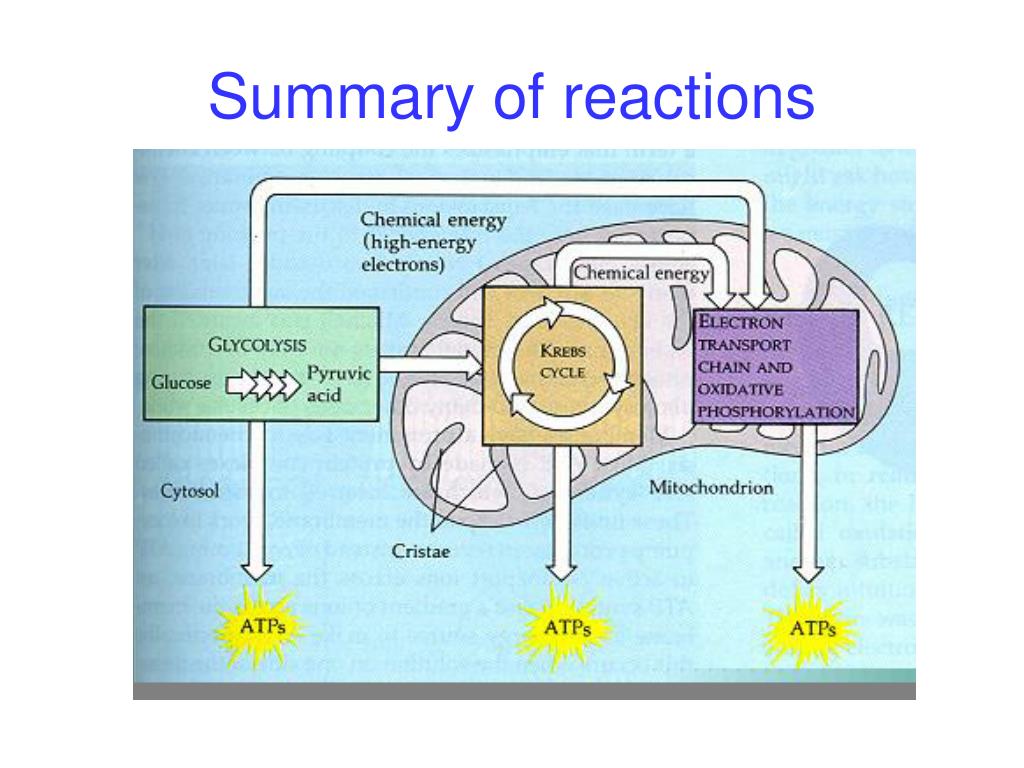 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
There are four stages to aerobic respiration: Cellular respiration describes how cells produce adenosine triphosphate (atp), which is cellular energy and can occur. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and the body cells, including inhalation and exhalation , diffusion of oxygen from the pulmonary alveoli to the blood and of carbon dioxide from the blood to the alveoli, followed by the transport of oxygen to and carbon dioxide from the. The cycle involves a series of changes in organic acids with 4‐, 5‐, and 6‐ carbon atoms (citric acid has 6 carbons). PPT Biology 3A respiration PowerPoint Presentation ID6264960.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Oxygen carried by blood is used in cellular respiration and carbon dioxide released combines with hemoglobin in rbcs. The first step in is glycolysis, the second is the citric acid cycle and the third is the electron trans port system. This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals. Aerobic respiration respiration using oxygen to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration. Respiration & gas exchange.
Most Of The Plant And Animal Cells Use Aerobic Respiration.
This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals. Thus, it is also called a citric acid cycle. Heterotrophic metabolism:.most familiar respiratory process (aerobic respiration) uses oxygen as the final electron acceptor. As already stated, cellular respiration can be of two types:
This Type Of Respiration Is Common In Most Plants And Animals, Including Humans, Birds And Other Mammals.
Aerobic respiration is the process of producing cellular energy involving oxygen. Aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondria and the cytoplasm of the cell. Cellular respiration describes how cells produce adenosine triphosphate (atp), which is cellular energy and can occur. Aerobic respiration is the process through which glucose is burned or oxidised in the presence of oxygen to produce energy (atp).
If Oxygen Is Present, The Pyruvate Produced In Glycolysis Is Oxidized Further In The Krebs Cycle, A Continuation Of Aerobic Respiration.
Respiration is also a cellular process. Deoxygenated or impure blood is carried by veins to the lungs to be converted into oxygenated blood. Therefore, aerobic respiration is the process of cellular respiration that uses oxygen to produce energy from food. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, whereas anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen.
Oxygen Carried By Blood Is Used In Cellular Respiration And Carbon Dioxide Released Combines With Hemoglobin In Rbcs.
Molecular oxygen is the most efficient electron acceptor for respiration, due to. Glycolysis, the link reaction, the krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. This is in contrast to the highly efficient process of aerobic respiration, which relies on oxygen to produce energy. The sugar is completely broken down to carbon dioxide and water, yielding a maximum of 38 molecules of atp per molecule of glucose.







